Report on the role of computer games in surviving self-isolation. Part 2/2
- May 20, 2020
- Dawid Zalewski
The previous part of our report presented conclusions from the study of changes in players’ habits since the introduction of mobility restrictions and the start of the #stayathome campaign. This time, we will look at the popularity of specific game genres during the epidemic. We analyzed data from Steam Spy – a tool used to track video game sales trends provided by a leading video game digital distribution service.
How we analyzed player preferences
In the first stage of research, we analyzed player declarations. We asked the players to list three game genres they played during and before isolation. However, the declarations alone gave us no information about how their behavior changed. To gain better insights into the impact of the pandemic on the popularity of individual types of games, we used the figures provided by Steam Spy.
What game are the players playing during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Between April 2019 and April 2020, we observed an increase in interest in specific genres we selected. The popularity of selected genres grew by 52%. At the same time, between January and April 2020, interest in video games increased by as much as 70%! Conclusion: coronavirus clearly influenced the choices of players.
Which game genres were exceptionally popular during the pandemic?
From January to April, i.e. during the increased spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, publishers of plague-related (150%) and multiplayer (100%) games saw the biggest increase in interest. On the other hand, RPG games recorded the biggest decrease (24%). Interestingly, the result was still better compared to last year’s figures.

These results confirm our original conclusions from the previous part of this report: here is a growing interest in bio-threat themed games.
It is also evident that, according to the report on the impact of the virus on sales,
players are more willing to play multiplayer games,
which meet some of their social needs. Compared to April 2019, players are more willing to play puzzle games (90% increase) and simulators (78%). Multiplayer and plague-related games achieved a 56- and 32-percent increase in interest, respectively. With a sizeable 46% drop, sports games have seen a marked decrease in interest.
It is worth remembering, however, that since sports games are released annually, many players may have purchased a newer edition of their favorite game (e.g. F1 2019 instead of the F1 2018 which we included in the study, or NBA 2k20 instead of NBA 2k19).

Do we play more?
There is no clear answer. Although we have seen a six percent increase in time spent on gameplay compared to a similar period last year, the trend has been decreasing since the beginning of this year – compared to January 2020, players are spending 10% less time on gameplay.
In the period from January to April, sports games saw the biggest increase in playing time – as much as 162%! This is an interesting phenomenon, given the decrease in the number of players choosing this genre. It seems that, even though the number of sports games fans declined, the most die-hardy were even more active than before.

The results for plague-related games are interesting. Although the genre saw a 39% decrease in playing times compared to the same period a year ago, the figures have increased by 32% since January 2020.
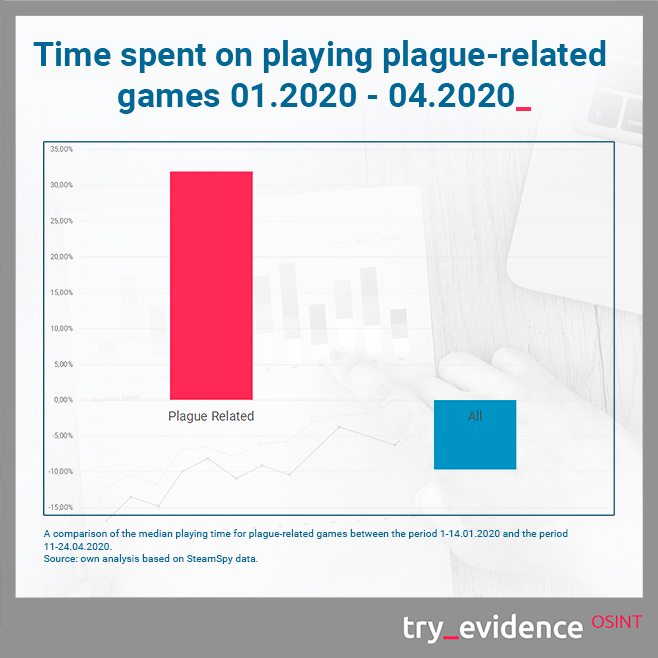
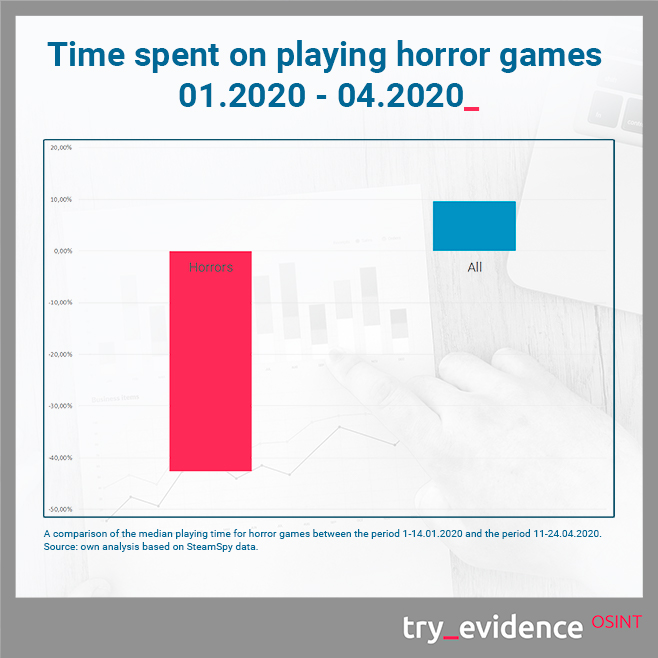
Horror statistics look equally interesting. Even though in relation to April last year, players devoted 5% more time to them, we noticed a significant decrease in the popularity of horror games since January this year. Perhaps, surrounded by the news about the effects of the virus and experiencing negative emotions and stress in connection with self-isolation, players avoid games focused on the feeling of anxiety, tension and fear.
Could players want to play plague-related games to familiarize with or better understand epidemic threats, but prefer to avoid excessive feeling of fear?
The classification of some games turned out to be problematic, as we could only assign one genre to each game. As a result, Resident Evil 2 was classified as an epidemic-themed game, even though it also contains elements of horror.
We checked, however, that had the game been considered in the horror category – the decrease in their popularity would have been smaller by 10 percentage points. Regardless, players in self-isolation are not willing to spend a lot of time on games of this kind.
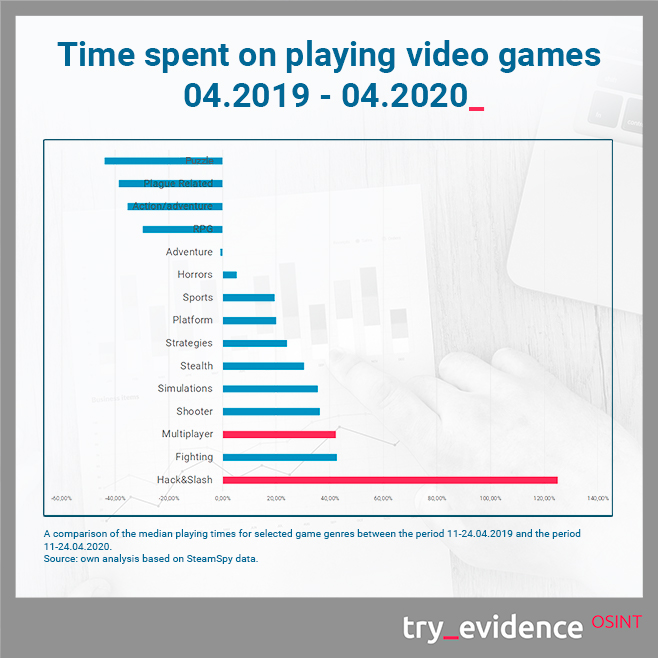
An analysis of the results from April 2019 and 2020 allows to conclude that players play the hack & slash games for the longest periods of time – up to 125% more than in a similar period a year ago. It can be a way for them to channel the negative emotions associated with the current situation, especially considering the statements of respondents from the previous section that they use games to cope with stress. However, the largest decrease in playing time (by as much as 44%) can be seen in puzzle games.
Summary – how did the Wuhan virus change gaming?
According to our analysis, the number of players increased. Self-isolation is associated with more free time – either due to unemployment, elimination of commute, or decreased social activities. But why is the growing number of Steam users not translating into more hours spent on interactive entertainment?
We suppose that regular players were joined by a cohort of people who, due to day-to-day responsibilities, could not play prior to the epidemic. Because games may have been only a casual form entertainment for them, they did not previously impact global statistics. Since such players still do not spend much time on games and hardcore gamers are playing even more than before, the average playing time is evening out.
Games from the plague-related category seem to be gaining popularity due to the current situation, as do multiplayer games, which for many people can become a substitute of social interactions.
Horror films are another interesting case. A clear drop in their popularity may be caused by the general deterioration of well-being among players, which was supported by the results of research from the previous section of the report.
*
The two parts of our report allow a clear conclusion – the virus had a significant impact on players.
Deteriorated mood, longing, lack of social contact and experienced stress changed players’ choices and habits.
It also turned out that games make this difficult time much easier for players – they help them maintain the recommended distance and make their days at home more enjoyable.
The increase in popularity of multiplayer games suggests that for some players online contact can be a substitute for social contacts. On the other hand, interest in plague-related games may indicate that although people are fed up with the news about the virus, the epidemiological threat still arouses their curiosity.
For many people, games are a way to deal with stress, which can explain the low interest in horror movies, which base on the feelings of fear and anxiety.
More and more people notice that gaming is an interesting and safe way of spending free time, and game developers are meeting the growing demand for virtual entertainment.
Annex: Methodology
The comparison of statistics from the month before isolation (January 2020) with the month of the most restrictive mobility restrictions (April 2020) showed us the changes in player behavior caused by the coronavirus pandemic. To best understand the changes, we compared this year’s trend changes with the results for the same period last year, i.e. April 2019.
We created a list of games broken down into categories. The titles we chose were supposed to best represent a group of epidemic and bio-threat themed settings from the report we published mid-March.
We measured interest in selected titles, comparing the maximum number of players playing a given title simultaneously during a given day over a two-week period.
To analyze the time players spent on entertainment, we used the median time that all players spent playing a specific game over the period of two weeks.







